As electric vehicle (EV) adoption continues to grow, the need for efficient, accessible, and reliable charging infrastructure becomes increasingly important. In North America, two primary charging connector standards dominate the EV charging landscape: the J1772 connector and the Tesla-developed North American Charging Standard (NACS). While both aim to facilitate seamless charging experiences, they differ significantly in terms of compatibility, functionality, and performance. In this article, we will explore the key differences between the J1772 and NACS charging standards, their respective advantages and drawbacks, and what these differences mean for EV owners.
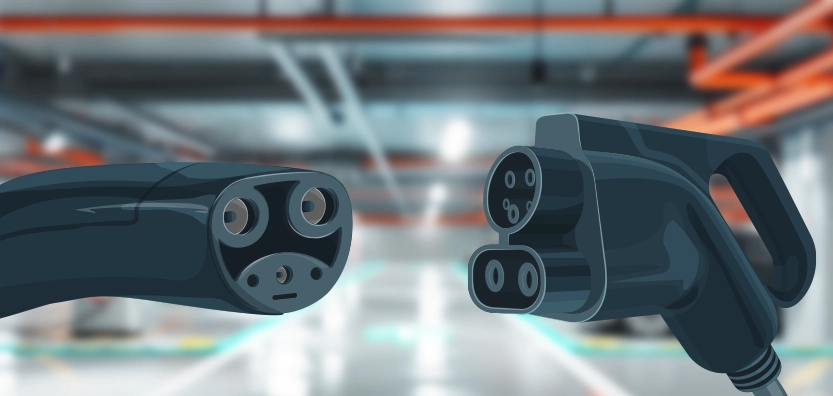
The J1772 charging standard, formally known as the SAE J1772 connector, is the industry-standard plug for non-Tesla electric vehicles (EVs) in North America. Introduced by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), the J1772 connector is widely used across various electric vehicle models from manufacturers like Chevrolet, Nissan, and BMW, among others.
The J1772 standard is primarily used for Level 1 (120V) and Level 2 (240V) AC charging, making it the go-to connector for everyday EV charging. For non-Tesla EV owners, the J1772 plug is the most common charging connector available across public charging stations.

The J1772 connector is compatible with a wide range of EV models across North America. Nearly all non-Tesla electric vehicles use this connector, making it a highly versatile and universal charging solution for EV owners.
J1772 connectors are designed with several safety features to protect users and vehicles during charging. These include ground fault detection, short circuit protection, and an automatic locking mechanism during charging, ensuring that both the vehicle and the charger are safe during the entire process.
The J1772 connector is straightforward to use. Its design is ergonomic and easy to plug into the vehicle, offering a hassle-free charging experience for EV owners.
One of the major advantages of J1772 is its widespread adoption. The connector is integrated into the majority of public charging stations and is commonly found in both home charging setups and public EV charging locations.
J1772 connectors have been around for many years and have proven themselves to be reliable and durable. They offer a stable charging process, making them a trusted option for everyday EV charging needs.
While J1772 supports both Level 1 and Level 2 charging, it is not designed for fast DC charging. As a result, J1772 chargers can be significantly slower than their DC fast charging counterparts, such as Tesla’s Superchargers or CCS chargers, which can result in longer charging times.
Some users have expressed concerns over the physical durability of the J1772 connector, particularly its locking mechanism. With regular use, wear and tear may cause the connector to become less secure, potentially affecting charging performance.
The J1772 standard is gradually becoming outdated as demand for faster charging and advanced features grows. While it has served EV owners well for many years, the connector may face challenges as more advanced charging standards emerge.
The North American Charging Standard (NACS), developed by Tesla, is a newer charging connector standard that was introduced to simplify the charging process for Tesla owners. Originally known as the "Tesla charging connector," the NACS was designed to work exclusively with Tesla's electric vehicles. However, in November 2022, Tesla made a pivotal decision to open up the NACS standard for use by other automakers and public charging infrastructure providers.
NACS is distinct from the J1772 standard in several key ways, particularly in its ability to provide both AC and DC fast charging through a single, compact connector. Unlike J1772, which relies on separate connectors for AC and DC charging, NACS integrates both functionalities into one connector, providing a more streamlined and user-friendly charging experience.
In June 2023, SAE International announced that it would work to standardize NACS, further cementing its place as a key player in the EV charging landscape. The NACS connector is expected to be the future of fast, reliable EV charging in North America.

The NACS connector is designed to work not only with Tesla vehicles but also with other EV brands that adopt the standard. This universal compatibility is achieved through its integration with the ISO 15118 communication protocol, similar to the Combined Charging System (CCS) connector, allowing NACS to charge both Tesla and non-Tesla vehicles.
NACS allows EV owners to access Tesla’s expansive Supercharger network, which is one of the largest and most reliable networks in North America. This expanded access means that NACS users can charge their vehicles at thousands of locations, simplifying the overall charging experience.
One of the most notable features of NACS is its emphasis on fast charging. Tesla's Superchargers, which are based on NACS, support charging speeds of up to 250 kW, making them faster than many traditional AC charging stations. The ability to rapidly recharge EVs ensures that drivers can spend less time charging and more time on the road.
The NACS connector is smaller and more compact than the J1772 connector, making it easier to handle and store. The sleek design not only enhances its portability but also adds to the overall user experience by making the connector easier to insert and remove.
Tesla's NACS connector supports the “plug-and-charge” feature, which allows the EV to start charging as soon as the connector is plugged in, without the need for additional authentication steps. This makes the charging process even more seamless and convenient for Tesla owners.
Although NACS chargers are growing in number, they are still less widespread than J1772 connectors. While Tesla's Supercharger network has more NACS-compatible charging stations than many other DC fast charging networks, the overall number of locations still lags behind networks that support J1772, which is widely available across North America.
Tesla’s Superchargers, which utilize NACS, offer charging speeds up to 250 kW. While this is significantly faster than many J1772 chargers, it falls short of the 350 kW maximum offered by some CCS chargers. This means that while NACS provides excellent fast charging speeds, it is not the absolute fastest charging standard available.
When comparing the overall charging experience between NACS and J1772, several key factors come into play:
One of the most significant differences between the two connectors is charging speed. While J1772 is limited to Level 1 and Level 2 charging (typically up to 19.2 kW), NACS supports much faster DC fast charging, up to 250 kW at Tesla Superchargers. This makes NACS the superior choice for those looking for quick recharging, particularly on long road trips.
NACS offers greater convenience due to its ability to handle both AC and DC fast charging in one connector, whereas J1772 requires separate connectors for AC and DC charging. Additionally, Tesla’s extensive Supercharger network, accessible to NACS-equipped EVs, offers greater charging convenience for Tesla owners. However, J1772 remains the more universally accepted standard across North America, as it is supported by a wider variety of charging networks.
J1772 has the advantage when it comes to availability, as it is supported by most public charging stations across North America. In contrast, NACS, although expanding rapidly, is still primarily available at Tesla’s Supercharger stations, which are fewer in number compared to stations supporting J1772.
The costs associated with NACS and J1772 chargers vary depending on location, provider, and charging speed. However, Tesla’s Superchargers (NACS) tend to have higher per-kWh rates for non-Tesla users, while J1772 charging stations are often more affordable, especially for Level 2 charging.
Both the J1772 and NACS charging standards offer significant advantages, depending on the needs and preferences of the EV owner. J1772 remains the dominant connector for non-Tesla vehicles and is widely available across North America, offering reliable and cost-effective charging solutions. On the other hand, NACS provides faster charging speeds, a more streamlined charging experience, and greater compatibility with Tesla’s Supercharger network, making it the preferred choice for Tesla owners and those looking for ultra-fast charging options.
Ultimately, the decision between NACS and J1772 depends on the vehicle you drive, your charging preferences, and the infrastructure available in your area. As the EV market continues to evolve, both standards will play critical roles in shaping the future of electric vehicle charging in North America.