As electric vehicles (EVs) continue to gain popularity, understanding the various charging connector types has become essential for both current and prospective EV owners. Charging connectors are not one-size-fits-all; they vary depending on the type of charging (AC or DC), the region, and the vehicle manufacturer. This article delves into the different EV charging connector types, their functionalities, and their compatibility with various EVs. Whether you're charging at home, at work, or on the go, knowing the right connector for your EV can make your charging experience seamless and efficient.
AC, or alternating current, is the most common form of EV charging and is widely used for daily charging needs. AC charging is typically divided into two levels: Level 1 and Level 2. These charging levels cater to different needs, from overnight home charging to faster top-ups at public stations.
Level 1 charging is the simplest and most accessible form of EV charging. It involves plugging your EV into a standard 120-volt household outlet using the cable that comes with your vehicle. While convenient, Level 1 charging is relatively slow, adding only about 3 to 5 miles of range per hour. This makes it ideal for overnight charging or for drivers with shorter daily commutes. However, for those who need faster charging, Level 2 is the preferred option.
Level 2 charging operates at 240 volts and is significantly faster than Level 1, delivering up to 40 miles of range per hour. This type of charging requires a dedicated charging station, such as the LiCB Charge, which can be installed at home or found at public charging locations like shopping centers, workplaces, and parking garages. Level 2 charging is the go-to option for most EV owners, as it strikes a balance between speed and accessibility.
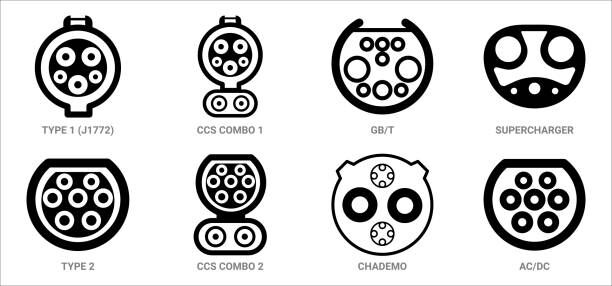
In North America, two primary connector standards are used for AC charging: SAE J1772 and the North American Charging Standard (NACS).
SAE J1772: This is the standard connector for most non-Tesla EVs in North America. It is compatible with both Level 1 and Level 2 charging and is widely available at public charging stations.
NACS (Tesla Connector): Developed by Tesla, the NACS connector is used exclusively for Tesla vehicles. However, Tesla has made efforts to open its charging network to other EVs, which could increase the adoption of this standard in the future.
While AC charging is sufficient for daily use, DC fast charging is the preferred option for long-distance travel or when you need a quick charge. DC, or direct current, bypasses the vehicle's onboard charger and delivers power directly to the battery, enabling significantly faster charging times.
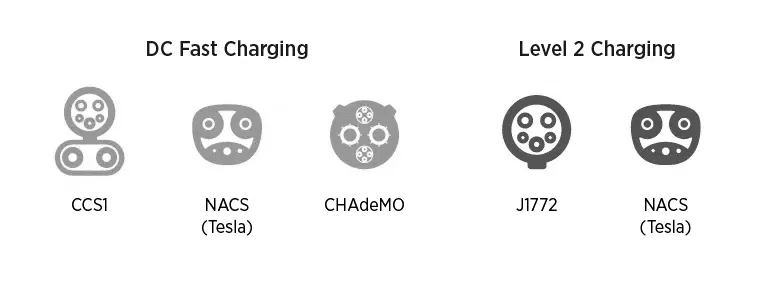
In North America, there are three main types of DC fast charging connectors: SAE Combo (CCS1), CHAdeMO, and NACS. Each connector type has its own unique features and compatibility requirements.
SAE Combo (CCS1): The Combined Charging System (CCS) is a versatile connector that combines AC and DC charging capabilities. CCS1, used in North America, is an evolution of the SAE J1772 connector with two additional DC pins at the bottom. It supports power levels of up to 350 kW, making it one of the fastest charging options available.
CHAdeMO: Developed in Japan, the CHAdeMO connector is another DC fast charging standard. While it was once widely used, its popularity has declined in recent years due to the growing adoption of CCS. However, some older EVs, particularly those from Japanese manufacturers, still use CHAdeMO connectors.
NACS (Tesla Connector): Tesla's NACS connector is unique in that it supports both AC and DC fast charging. While it is primarily used by Tesla vehicles, the company's decision to open its Supercharger network to other EVs could lead to broader adoption of this standard.
As EV technology advances, the demand for faster charging solutions has led to the development of high-power DC chargers. While 50 kW chargers are still common, 150 kW, 270 kW, and even 350 kW chargers are becoming increasingly available. These high-power chargers can add hundreds of miles of range in just minutes, making them ideal for long-distance travel.
The Combined Charging System (CCS) has emerged as the leading DC fast charging standard worldwide. Its elegant design and high power capabilities have made it a favorite among automakers and charging network operators.
CCS connectors come in two variants: Type 1 and Type 2.
CCS Type 1: This variant is used primarily in North America and is based on the SAE J1772 connector. It features two additional DC pins at the bottom, enabling fast DC charging.
CCS Type 2: Used in Europe, CCS Type 2 is based on the Mennekes Type 2 connector. Like its North American counterpart, it includes two extra DC pins for fast charging.
One of the key advantages of CCS is its ability to support both AC and DC charging through a single connector. This eliminates the need for multiple charging ports on the vehicle, simplifying the design and reducing costs. Additionally, CCS connectors can handle power levels of up to 350 kW, making them suitable for the latest generation of high-power chargers.
Despite its many benefits, CCS is not without its challenges. For example, CCS connectors are not compatible with CHAdeMO or GB/T charging stations, as these systems use different communication protocols. While adapters are available, they can be difficult to obtain and may not always provide a seamless charging experience.
While CCS has become the dominant DC fast charging standard, CHAdeMO remains an important option for certain vehicles. Developed by a consortium of Japanese companies, CHAdeMO was one of the first DC fast charging standards and is still used by some older EVs.
Bidirectional Charging: One of the unique features of CHAdeMO is its support for bidirectional charging, which allows the vehicle to send power back to the grid or to a home. This capability is particularly useful for vehicle-to-grid (V2G) applications.
Compatibility: CHAdeMO connectors are not compatible with CCS or GB/T charging stations, which can limit their usability in regions where these standards are dominant.
As CCS continues to gain traction, the future of CHAdeMO is uncertain. However, it remains an important option for certain vehicles, particularly those from Japanese manufacturers. Additionally, its bidirectional charging capabilities could ensure its relevance in niche applications.
In China, the GB/T standard is the dominant charging connector for both AC and DC charging. Developed by the Chinese government, GB/T connectors are used by most EVs sold in the country.
AC and DC Charging: Like CCS, GB/T connectors support both AC and DC charging, making them versatile and convenient for EV owners.
High Power Capabilities: GB/T connectors can support power levels of up to 250 kW, making them suitable for fast charging applications.
While GB/T is primarily used in China, its influence is growing as Chinese automakers expand into global markets. However, its incompatibility with CCS and CHAdeMO could limit its adoption outside of China.
Tesla's North American Charging Standard (NACS) is a unique connector that supports both AC and DC fast charging. While it is primarily used by Tesla vehicles, the company's decision to open its Supercharger network to other EVs could lead to broader adoption of this standard.
Compact Design: The NACS connector is smaller and more compact than CCS or CHAdeMO, making it easier to handle and install.
High Power Capabilities: NACS connectors can support power levels of up to 250 kW, making them suitable for fast charging applications.
While NACS is currently limited to Tesla vehicles, the company's efforts to open its charging network to other EVs could increase its adoption. However, its proprietary nature and incompatibility with other standards could limit its appeal to non-Tesla automakers.
As the EV market continues to evolve, understanding the different charging connector types is essential for maximizing your charging experience. Whether you're using AC charging for daily needs or DC fast charging for long-distance travel, choosing the right connector can make all the difference. With the growing availability of high-power chargers and the increasing standardization of connectors, the future of EV charging looks brighter than ever. By staying informed and choosing the right charging solution for your needs, you can enjoy the full benefits of electric vehicle ownership.