On this page
With the growing popularity of electric vehicles (EVs) around the world, more and more drivers are choosing this environmentally friendly mode of transportation. However, the data shows that about 20% of electric vehicle owners will experience charging problems at some point. One of the most common and vexing problems is that electric vehicles don't charge properly. Imagine this scenario. You've planned a long trip, set off ready and expectant, but when you stop at the charging station and plug in the charger, the charging device doesn't respond. This frustrating scene highlights the importance of understanding the EV charging process and effectively troubleshooting it. This guide will help you navigate common charging challenges and ensure your electric vehicle always runs smoothly.
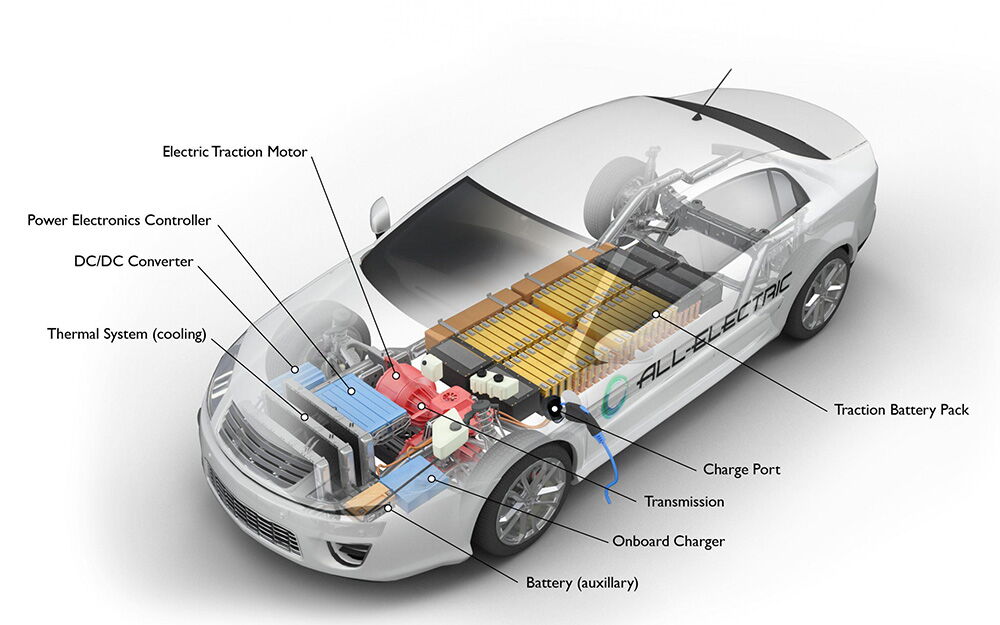
To successfully deal with the charging problem of electric vehicles, we first need to understand the basic principles of electric vehicle charging. When an electric car is connected to a power supply via a charging cable, electricity flows from the power supply to the charging station and then into the car's battery to charge it. There are three main levels of electric vehicle chargers: Tier 1, which uses a standard 120V socket, is the slowest to charge and typically takes about 20 hours to fully charge; The secondary charger uses 240V socket, charging speed is fast, generally takes 4-8 hours; Level 3 charger (DC Fast charger) can charge the battery to 80% in 30 minutes. Charging times are affected by a number of factors, including the type of charger, the capacity of the car's battery, and the current battery charge. In addition, extreme temperature conditions will also have an impact on the charging efficiency. Understanding these basics will help identify and resolve potential charging problems more effectively.
 Hardware failures are common causes of charging problems and can include faulty charging cables or connectors as well as problems with the charging station itself. For example, damage to the charging port may prevent the car from establishing a stable connection, thus hindering the charging process. Owners are advised to check charging devices regularly for early detection of physical damage.
Software glitches can also cause charging failures. The on-board software of electric vehicles sometimes fails to communicate properly with the charging station, resulting in charging interruptions. Regular updates to vehicle and charging station software can help prevent these problems. If a software issue is suspected, performing a system reset or installing the latest update can often resolve the problem.
User error is also one of the common reasons for charging failure. Common mistakes include charging cables not being plugged in properly, using incompatible charging devices, or not activating a charging session with the necessary smartphone app or RFID card. Owners are advised to double-check all Settings to ensure proper connection and activation of the charging session.
Another reason the car charger doesn't work can be a problem with the battery itself. In this case, the battery may need to be repaired or replaced. In addition, some vehicles may stop charging when the battery is depleted, requiring manual operation to restart the charging process.
First check whether the home power supply system meets the power needs of the electric car charger. Make sure the circuit breaker is not tripping or the fuse is not blown, which can cause a power outage. Also, make sure the sockets you use are working properly. Next, check the charging cable connection to make sure both ends of the cable are fully plugged in. If the cable is improperly connected, charging may fail. Unplug the cable and plug it back in, making sure it is securely connected to the car's charging port and power outlet.
Hardware failures are common causes of charging problems and can include faulty charging cables or connectors as well as problems with the charging station itself. For example, damage to the charging port may prevent the car from establishing a stable connection, thus hindering the charging process. Owners are advised to check charging devices regularly for early detection of physical damage.
Software glitches can also cause charging failures. The on-board software of electric vehicles sometimes fails to communicate properly with the charging station, resulting in charging interruptions. Regular updates to vehicle and charging station software can help prevent these problems. If a software issue is suspected, performing a system reset or installing the latest update can often resolve the problem.
User error is also one of the common reasons for charging failure. Common mistakes include charging cables not being plugged in properly, using incompatible charging devices, or not activating a charging session with the necessary smartphone app or RFID card. Owners are advised to double-check all Settings to ensure proper connection and activation of the charging session.
Another reason the car charger doesn't work can be a problem with the battery itself. In this case, the battery may need to be repaired or replaced. In addition, some vehicles may stop charging when the battery is depleted, requiring manual operation to restart the charging process.
First check whether the home power supply system meets the power needs of the electric car charger. Make sure the circuit breaker is not tripping or the fuse is not blown, which can cause a power outage. Also, make sure the sockets you use are working properly. Next, check the charging cable connection to make sure both ends of the cable are fully plugged in. If the cable is improperly connected, charging may fail. Unplug the cable and plug it back in, making sure it is securely connected to the car's charging port and power outlet.
You should also check if the car has a delay timer or smart charging function set, which may cause charging to delay or fail to start. Adjust the Settings accordingly to ensure that charging can begin immediately. If these steps do not solve the problem, you can try to reset the charging station. Disconnect the charger and wait a few minutes before reinserting it, which can help clean up any temporary glitches in the system.
 First, verify the validity of the payment method and the RFID card. Make sure your payment method is working properly or your RFID card is working properly, as inactive account status or insufficient funds can cause transactions to fail and hinder the charging process. If the payment method and card are working, but the problem persists, you may need to solve the network connection problem. Public charging stations rely on the network for transactions and monitoring, and a poor network connection can interrupt charging. When this happens, try restarting the charging session or moving to a different charging station and report the connection issue to the carrier.
First, verify the validity of the payment method and the RFID card. Make sure your payment method is working properly or your RFID card is working properly, as inactive account status or insufficient funds can cause transactions to fail and hinder the charging process. If the payment method and card are working, but the problem persists, you may need to solve the network connection problem. Public charging stations rely on the network for transactions and monitoring, and a poor network connection can interrupt charging. When this happens, try restarting the charging session or moving to a different charging station and report the connection issue to the carrier.
If the issue remains unresolved, report the details to the charging station operator, providing the exact location of the charging station and any error messages. This will help operators perform remote diagnostics or send technicians to fix problems and ensure that charging stations can be used normally. Slow charging speed is one of the common troubles of electric vehicle owners, pay attention to the effect of battery temperature on charging speed. Extreme temperature conditions will slow down the charging speed, so try to charge in mild weather conditions to avoid reducing the charging efficiency of the battery or charging station due to overheating or cold. Avoid situations where you encounter shared loads at public charging stations, as the power from these stations is often distributed among multiple vehicles, potentially resulting in slower charging. Choosing less used charging stations can help alleviate this problem. Finally, keep the software of electric vehicles and charging stations updated to ensure they are compatible with the latest charging standards and improve charging efficiency. Tesla models: Tesla owners may experience on-board charger failures or connectivity issues with superchargers. Regular software updates and the use of officially certified chargers can improve reliability.
Nissan Leaf: Nissan Leaf owners may experience compatibility issues with the CHAdeMO charging system. Updating the software and using the recommended charger can help resolve these issues.
Chevy Bolt: Chevy Bolt owners may face challenges with charging ports or in-car charging systems. Common charging problems can be avoided by keeping charging ports clean and using recommended charging devices. To ensure the best performance and longevity of EV batteries, it is recommended to follow the following best practices: Use a dedicated charger and avoid the use of extension cords, which can lead to voltage drop and overheating risk; Avoid frequently charging the battery to 100%, it is recommended to keep the charge between 80% and 90% to extend the battery life; Keep vehicle and charging station software up to date to benefit from the latest features and improvements. By following these tips, you will be able to better manage the charging needs of your electric vehicle, ensure that the vehicle is always in top condition and enjoy a hassle-free driving experience. Keeping an eye on charging equipment and software, and resolving problems in a timely manner, will help you enjoy a more reliable and efficient electric vehicle experience. I hope this guide will provide you with valuable help to give you more peace of mind and convenience when using an electric vehicle.
 Hardware failures are common causes of charging problems and can include faulty charging cables or connectors as well as problems with the charging station itself. For example, damage to the charging port may prevent the car from establishing a stable connection, thus hindering the charging process. Owners are advised to check charging devices regularly for early detection of physical damage.
Software glitches can also cause charging failures. The on-board software of electric vehicles sometimes fails to communicate properly with the charging station, resulting in charging interruptions. Regular updates to vehicle and charging station software can help prevent these problems. If a software issue is suspected, performing a system reset or installing the latest update can often resolve the problem.
User error is also one of the common reasons for charging failure. Common mistakes include charging cables not being plugged in properly, using incompatible charging devices, or not activating a charging session with the necessary smartphone app or RFID card. Owners are advised to double-check all Settings to ensure proper connection and activation of the charging session.
Another reason the car charger doesn't work can be a problem with the battery itself. In this case, the battery may need to be repaired or replaced. In addition, some vehicles may stop charging when the battery is depleted, requiring manual operation to restart the charging process.
First check whether the home power supply system meets the power needs of the electric car charger. Make sure the circuit breaker is not tripping or the fuse is not blown, which can cause a power outage. Also, make sure the sockets you use are working properly. Next, check the charging cable connection to make sure both ends of the cable are fully plugged in. If the cable is improperly connected, charging may fail. Unplug the cable and plug it back in, making sure it is securely connected to the car's charging port and power outlet.
Hardware failures are common causes of charging problems and can include faulty charging cables or connectors as well as problems with the charging station itself. For example, damage to the charging port may prevent the car from establishing a stable connection, thus hindering the charging process. Owners are advised to check charging devices regularly for early detection of physical damage.
Software glitches can also cause charging failures. The on-board software of electric vehicles sometimes fails to communicate properly with the charging station, resulting in charging interruptions. Regular updates to vehicle and charging station software can help prevent these problems. If a software issue is suspected, performing a system reset or installing the latest update can often resolve the problem.
User error is also one of the common reasons for charging failure. Common mistakes include charging cables not being plugged in properly, using incompatible charging devices, or not activating a charging session with the necessary smartphone app or RFID card. Owners are advised to double-check all Settings to ensure proper connection and activation of the charging session.
Another reason the car charger doesn't work can be a problem with the battery itself. In this case, the battery may need to be repaired or replaced. In addition, some vehicles may stop charging when the battery is depleted, requiring manual operation to restart the charging process.
First check whether the home power supply system meets the power needs of the electric car charger. Make sure the circuit breaker is not tripping or the fuse is not blown, which can cause a power outage. Also, make sure the sockets you use are working properly. Next, check the charging cable connection to make sure both ends of the cable are fully plugged in. If the cable is improperly connected, charging may fail. Unplug the cable and plug it back in, making sure it is securely connected to the car's charging port and power outlet.You should also check if the car has a delay timer or smart charging function set, which may cause charging to delay or fail to start. Adjust the Settings accordingly to ensure that charging can begin immediately. If these steps do not solve the problem, you can try to reset the charging station. Disconnect the charger and wait a few minutes before reinserting it, which can help clean up any temporary glitches in the system.
 First, verify the validity of the payment method and the RFID card. Make sure your payment method is working properly or your RFID card is working properly, as inactive account status or insufficient funds can cause transactions to fail and hinder the charging process. If the payment method and card are working, but the problem persists, you may need to solve the network connection problem. Public charging stations rely on the network for transactions and monitoring, and a poor network connection can interrupt charging. When this happens, try restarting the charging session or moving to a different charging station and report the connection issue to the carrier.
First, verify the validity of the payment method and the RFID card. Make sure your payment method is working properly or your RFID card is working properly, as inactive account status or insufficient funds can cause transactions to fail and hinder the charging process. If the payment method and card are working, but the problem persists, you may need to solve the network connection problem. Public charging stations rely on the network for transactions and monitoring, and a poor network connection can interrupt charging. When this happens, try restarting the charging session or moving to a different charging station and report the connection issue to the carrier.If the issue remains unresolved, report the details to the charging station operator, providing the exact location of the charging station and any error messages. This will help operators perform remote diagnostics or send technicians to fix problems and ensure that charging stations can be used normally. Slow charging speed is one of the common troubles of electric vehicle owners, pay attention to the effect of battery temperature on charging speed. Extreme temperature conditions will slow down the charging speed, so try to charge in mild weather conditions to avoid reducing the charging efficiency of the battery or charging station due to overheating or cold. Avoid situations where you encounter shared loads at public charging stations, as the power from these stations is often distributed among multiple vehicles, potentially resulting in slower charging. Choosing less used charging stations can help alleviate this problem. Finally, keep the software of electric vehicles and charging stations updated to ensure they are compatible with the latest charging standards and improve charging efficiency. Tesla models: Tesla owners may experience on-board charger failures or connectivity issues with superchargers. Regular software updates and the use of officially certified chargers can improve reliability.
Nissan Leaf: Nissan Leaf owners may experience compatibility issues with the CHAdeMO charging system. Updating the software and using the recommended charger can help resolve these issues.
Chevy Bolt: Chevy Bolt owners may face challenges with charging ports or in-car charging systems. Common charging problems can be avoided by keeping charging ports clean and using recommended charging devices. To ensure the best performance and longevity of EV batteries, it is recommended to follow the following best practices: Use a dedicated charger and avoid the use of extension cords, which can lead to voltage drop and overheating risk; Avoid frequently charging the battery to 100%, it is recommended to keep the charge between 80% and 90% to extend the battery life; Keep vehicle and charging station software up to date to benefit from the latest features and improvements. By following these tips, you will be able to better manage the charging needs of your electric vehicle, ensure that the vehicle is always in top condition and enjoy a hassle-free driving experience. Keeping an eye on charging equipment and software, and resolving problems in a timely manner, will help you enjoy a more reliable and efficient electric vehicle experience. I hope this guide will provide you with valuable help to give you more peace of mind and convenience when using an electric vehicle.
