As electric vehicles become more popular, we need to understand the different charging methods for electric vehicles. This paper gives an overview of level 1, 2, and 3 charging methods, focusing on their key features, power requirements, charging speed, and compatibility. Whether you're a new EV owner or looking to upgrade your charging infrastructure, this guide will help you navigate the options and choose the best solution for your needs.
Level 1 charging is the slowest form of charging and is similar to charging your phone from a home wall outlet. It is ideal for charging overnight or for use when there is no urgent need. A full charge can take 24 hours or more, depending on the size and capacity of the battery.
Level 2 charging is much faster, the equivalent of replacing a garden hose with a fire hose. It uses 240V power, such as a clothes dryer socket, and can charge 12 to 80 miles per hour. This type of charging is ideal for users who regularly drive electric vehicles and is very common in public places, office buildings and homes.
Level 3 charging, that is, DC fast charging, is the fastest way to charge. It uses direct current (DC) and charges much faster than Level 2. In just 20 minutes, the electric car can travel 60 to 80 miles. However, not all electric vehicles support this kind of high-power charging, so compatibility is key.
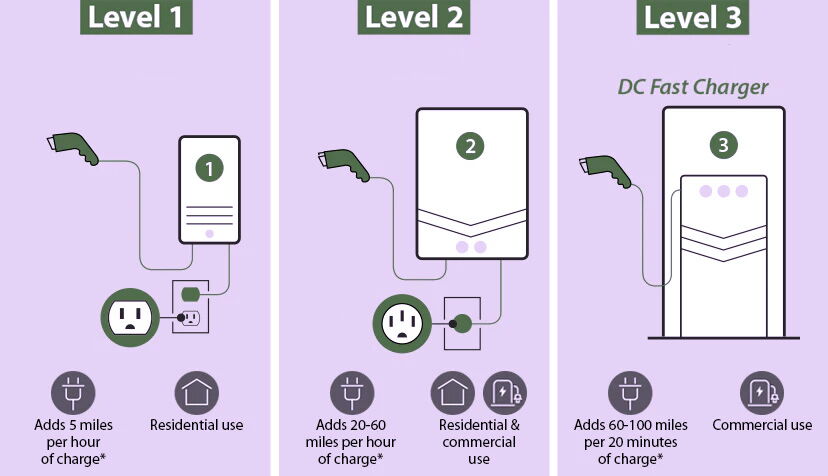
Level 1 charging power is between 1.4 and 1.9 kW, which is suitable for scenarios with low power requirements. It is powered through a North American standard 120 volt AC socket and is suitable for long charging periods, such as overnight charging. Although it is easy to obtain, it has limited effectiveness in fast charging and is suitable for situations where charging times are longer.
Level 2 charging power ranges from 3.3kW to 19.2kW, a boost that significantly speeds up charging. It uses 240-volt AC power, similar to a clothes dryer socket, and is suitable for scenarios that require frequent charging. Level 2 charging is efficient without placing an excessive burden on the grid and is suitable for residential and public charging infrastructure.
Level 3 charging power ranges from 50 kW to 350 kW and is capable of charging an electric vehicle up to 80% in a short time. This kind of high-power charging requires advanced equipment and electrical frameworks, usually found in dedicated EV charging stations. Although charging speeds are extremely fast, the demands on the grid are also high and require careful planning.
Level 1 charging offers a range of 2 to 5 miles per hour, making it ideal for overnight charging or short drives. The charging speed is slow and is not suitable for scenarios that require fast charging.
Level 2 charging provides a range of 12 to 80 miles per hour and is suitable for electric vehicles parked at home or in public Spaces for long periods of time. For EVs with 60 kWh batteries, a full charge via a level 2 charger typically takes 4 to 10 hours.
Level 3 charging gives EVs a range of 60 to 80 miles in 20 minutes, making it ideal for long trips or time-pressed scenarios. It should be noted that the speed of level 3 charging depends on the charging acceptance capacity of the vehicle and the battery structure.
Level 1 and 2 charging systems make extensive use of J1772 connectors, and most electric vehicles support these charging methods. However, Level 3 charging involves Tesla Superchargers, CHAdeMO, and combined charging systems (CCS), and compatibility is more complex. Tesla chargers are designed for Tesla models, CHAdeMO is mainly used in vehicles from Japanese manufacturers such as Nissan and Mitsubishi, and CCS is increasingly popular in Europe and the United States. It is important to understand the charging specifications and compatibility of the vehicle to ensure efficient use of the charging facilities.
Level 1 charging is suitable for homes and places with long parking periods, such as offices. This charging method is very suitable for owners who charge at night or have little daily driving needs.
Level 2 charging is suitable for places that require fast charging, such as shopping malls, office buildings and public parking lots. It shortens charging time and is suitable for vehicles parked for long periods of time.
Level 3 charging is suitable for public places that require fast charging, such as along highways, urban centers, and high-traffic areas. This charging method provides great convenience for long-distance travelers.
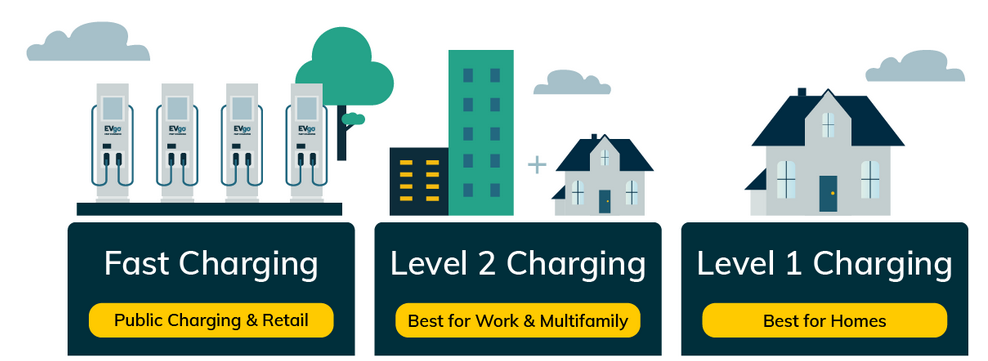
Choosing the right charging level takes into account customer needs and facility capabilities. If the customer usually stays in the venue for a long time, such as a hotel or retail complex, it is recommended to install a level 2 charging facility. These systems offer a balance of efficiency and convenience.
If fast service is essential (such as roadside facilities or fast food restaurants), it is more appropriate to choose a level 3 charging facility. Despite the need for more investment and infrastructure improvements, Level 3 charging is able to provide faster charging speeds to meet time-critical needs.
Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of each charging level and their applicable scenarios can help you choose the most appropriate charging solution to meet the needs of different users. Whether for home use or commercial applications, choosing the right charging facility can not only enhance the experience of electric vehicles, but also lay the foundation for the popularization of electric vehicles in the future.
