Electric vehicles (EVs) and EV chargers have surged in popularity, driven by advancements in battery technology, environmental concerns, and government incentives promoting clean energy. Among the most critical components of an EV is its battery pack, which powers the vehicle and significantly impacts its overall cost and performance. This comprehensive guide explores how EV batteries work, their longevity, replacement costs, and factors influencing their price, while also highlighting the role of EV chargers in ensuring efficient and reliable charging solutions.
The vast majority of electric vehicles on the market today are powered by lithium-ion batteries. Despite ongoing research into alternative chemistries and prototypes, lithium-ion technology remains the gold standard for EVs due to its established production infrastructure and proven efficiency. Let’s examine why lithium-ion batteries dominate the EV landscape:
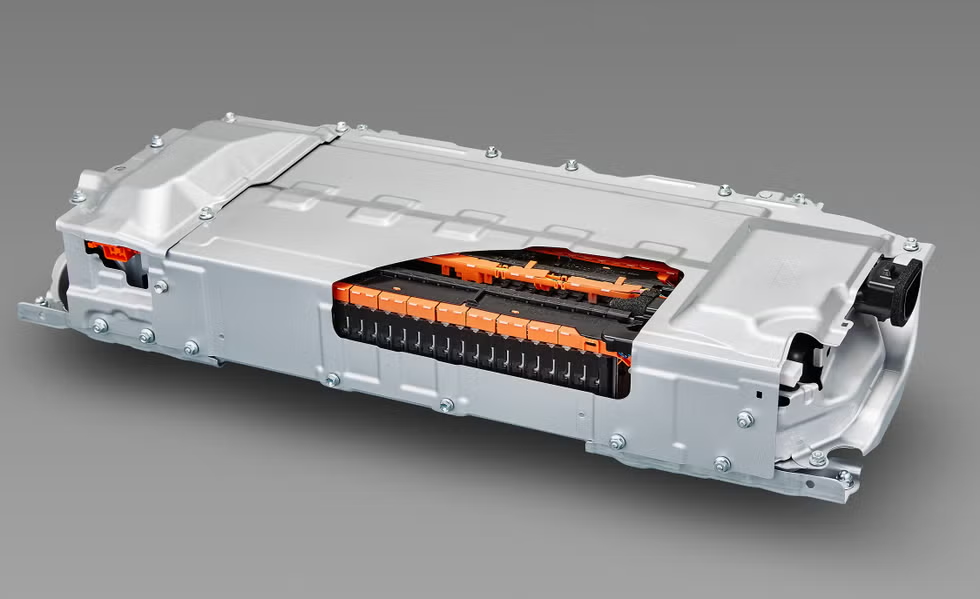
Lithium-ion batteries offer a superior energy density compared to other types of batteries. This means they can store more energy in a smaller, lighter package, allowing EVs to achieve longer ranges. For comparison, lead-acid batteries, commonly used in conventional vehicles, and nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries, often found in hybrid models, fall short in energy density.
Lithium-ion batteries self-discharge at a much lower rate than their counterparts. Under moderate climate conditions, they lose only 1–2% of their charge per month, ensuring they remain functional and efficient even after extended periods of non-use.
Unlike older battery technologies, lithium-ion batteries do not require full discharges to maintain optimal performance. Additionally, they eliminate the need for electrolyte maintenance, making them user-friendly and cost-effective in the long term.
Even as a lithium-ion battery's charge depletes, it provides consistent voltage output. This ensures steady and reliable performance for the EV, which is crucial for driver confidence and safety.
While lithium-ion batteries dominate the EV market, other battery types are occasionally used for specific applications or complementary purposes:
Known for their high power capabilities, NiMH batteries are used in some hybrid vehicles. However, they are less suitable for EVs due to their higher self-discharge rates and excessive heat generation in warm environments.
These are typically used for ancillary systems in EVs, such as powering lights and other secondary loads. Their short lifespan and low energy density make them unsuitable for primary propulsion systems.
Often paired with traditional batteries, ultracapacitors provide bursts of power during acceleration or when climbing steep inclines. They are also useful for storing secondary energy, enhancing overall vehicle efficiency.
Battery longevity is a critical consideration for both automakers and consumers. Fortunately, modern EV batteries are built to last, and manufacturers back this up with robust warranties:
Automakers typically offer an eight-year or 100,000-mile warranty on EV battery packs. This reflects their confidence in the durability of lithium-ion technology.
Tesla, a leader in the EV market, provides an eight-year warranty with coverage varying between 100,000 and 150,000 miles, depending on the vehicle model. Importantly, Tesla guarantees that its batteries will retain at least 70% of their capacity during the warranty period. If the capacity drops below this threshold, Tesla replaces the battery pack at no cost to the owner.
Over time, all lithium-ion batteries lose a small fraction of their capacity due to repeated charge cycles. However, this degradation is typically slow and manageable, allowing most EV owners to enjoy reliable performance for years before noticing any significant decline.
Battery replacement costs can be a concern for EV owners, but such expenses are rare due to long warranties and the durability of modern batteries. Here's what you need to know:
Outside of warranty coverage, replacing an EV battery can cost anywhere from $5,000 to $16,000, depending on the battery size, capacity, and manufacturer. For instance, luxury EVs with larger battery packs may incur higher replacement costs.
For new EV buyers, the chances of needing a battery replacement during the vehicle's lifespan are minimal. Even used EV buyers can rest assured that most batteries will remain within acceptable performance levels for many years.
Before purchasing a used EV, it’s wise to verify the battery’s health. Services like Recurrent Battery Health Reports provide detailed insights into a battery's condition, offering peace of mind to prospective buyers.
If a battery replacement becomes necessary, there are several options to reduce costs:
Refurbished batteries, which are reconditioned for optimal performance, offer a budget-friendly alternative to new battery packs.
Salvaged EVs can provide used batteries that still retain sufficient capacity for practical use. This option is particularly appealing for older or less expensive EV models.
In some cases, individual battery modules can be repaired or replaced, avoiding the need for a complete battery pack replacement.
Several variables affect the price of EV batteries, making it essential for consumers to understand the factors at play:
The specific chemistry of a battery, such as lithium-ion or nickel-metal hydride, significantly impacts production costs.
Larger batteries with greater energy capacities require more raw materials, resulting in higher costs. This is why long-range EVs are typically more expensive than their shorter-range counterparts.
Essential elements like lithium, cobalt, and nickel are critical to battery production. Fluctuations in global supply and demand for these materials can influence battery prices.
Advances in battery production processes and economies of scale have steadily reduced costs, making EVs more affordable for consumers.
Proper maintenance is crucial to extending the lifespan of an EV battery. While most EVs come equipped with advanced battery management systems (BMS), there are additional steps owners can take:
Many EVs house their battery packs under the vehicle floor, making them vulnerable to damage from road debris or accidents. Careful driving and routine inspections can help prevent such issues.
Extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, can degrade battery performance. Parking in shaded areas during summer and preconditioning the vehicle in winter can mitigate temperature-related wear.
Keeping your EV’s software up-to-date ensures the battery management system operates efficiently, maximizing battery health and performance.
Avoiding frequent full discharges or overcharging can help preserve battery longevity. Most EVs allow owners to set a charging limit to prevent unnecessary strain on the battery.
While lithium-ion technology currently dominates, the future of EV batteries is filled with promise. Innovations such as solid-state batteries aim to deliver even greater energy density, faster charging times, and enhanced safety. However, widespread adoption of these technologies will depend on overcoming production challenges and achieving cost parity with existing solutions.
In the meantime, lithium-ion batteries continue to evolve, with improvements in energy efficiency, durability, and recyclability. As production scales up and new technologies emerge, EV batteries are expected to become more affordable, further accelerating the global shift toward electric mobility.
The cost of an electric car battery is influenced by numerous factors, from its chemistry and capacity to raw material prices and manufacturing efficiency. Despite the potential expense of replacements, most EV owners are unlikely to face such costs thanks to generous warranties and the long lifespan of modern batteries.
As technology advances, battery costs are expected to decrease, making EVs even more accessible. Whether you’re considering a new or used electric vehicle, understanding how batteries work, their expected lifespan, and the factors affecting their price will help you make an informed decision and enjoy the many benefits of EV ownership.