As electric vehicles (EVs) become an increasingly mainstream choice for drivers worldwide, more homeowners are considering the installation of home charging equipment to support daily use. Among the many available charging options, the 30-amp (30A) Level 2 EV charger stands out as one of the most common and cost-effective solutions for residential and small business users. But is 30 amps really enough to meet your charging needs? How does it compare to other EV charger types in terms of performance, speed, and efficiency?
This article explores in depth what a 30A EV charger is, how fast it charges, what electrical setup it requires, and whether it’s the right fit for your electric vehicle and lifestyle.
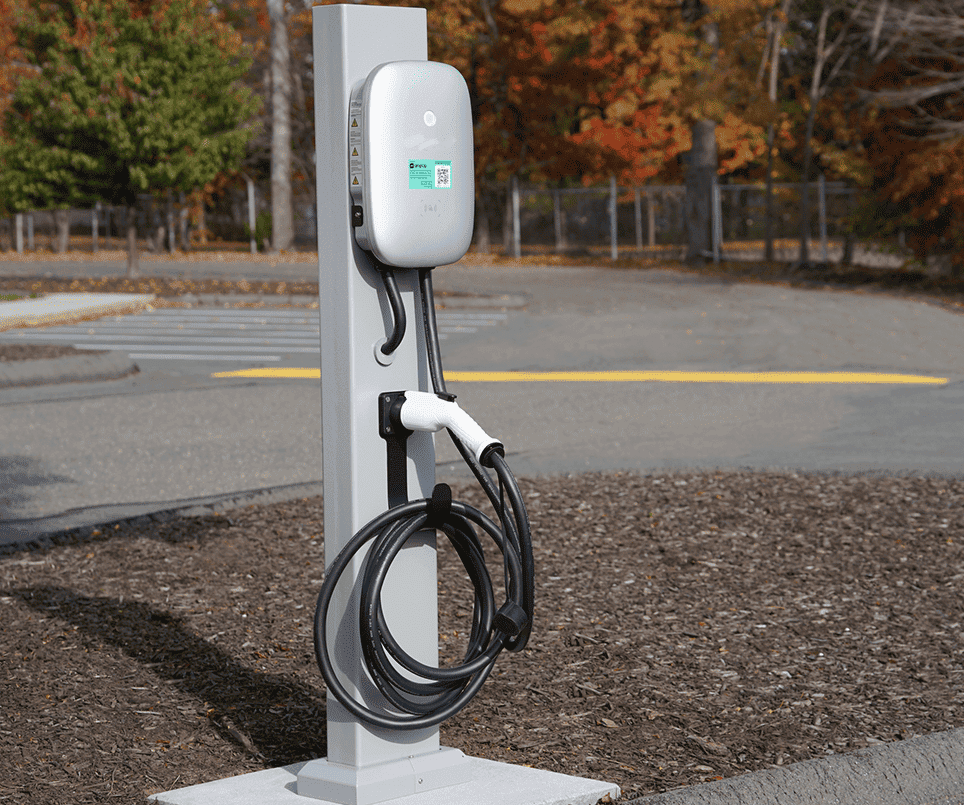
A 30A EV charger is a typical Level 2 electric vehicle charging device, designed to operate on a 240-volt circuit. It can safely and steadily deliver up to 30 amps of current, translating to around 7.2 kilowatts (kW) of power output, depending on the setup. This configuration offers a substantial upgrade in charging efficiency compared with Level 1 chargers that rely on a standard 120-volt household outlet.
Equipped with a J1772 connector — the universal standard for most EVs in North America — the 30A Level 2 charger provides wide compatibility across different vehicle brands. Whether it’s a Tesla (with an adapter), a Nissan Leaf, or a Ford Mustang Mach-E, this charger can seamlessly recharge a range of electric cars.
To operate properly, the 30A charger requires a dedicated 240V circuit breaker, typically installed by a licensed electrician. It can be mounted in garages, driveways, office parking lots, or small commercial locations, and many models are rated for both indoor and outdoor use, offering flexibility in installation.
Compared with the slow, portable Level 1 charger that often comes with EVs, a 30A charger can dramatically reduce charging time. It can add approximately 20–25 miles of range per hour, depending on the vehicle and battery efficiency, enabling most EV owners to fully recharge overnight — a major convenience for daily commuting.
Even more importantly, installing a 30A EV charger doesn’t typically require major upgrades to your home’s electrical infrastructure. It provides an excellent balance between performance and cost, making it a preferred option for most residential users.
The charging speed of an EV charger depends on three primary factors: the current (amperage), the voltage, and the vehicle’s onboard charger capacity. In the case of a 30A charger, the maximum output is about 7.2 kW (240 volts × 30 amps). However, due to safety rules set by the National Electrical Code (NEC), continuous loads like EV chargers are limited to 80% of the circuit’s rated capacity. This means a 30A charger usually draws 24A continuously, yielding around 5.8 kW of usable charging power.
So, what does that mean in practical terms?
Range added per hour: 18 to 22 miles
Time for full charge (60 kWh battery): about 10–11 hours
Time for top-up charge (20–80%): around 6 hours
This makes the 30A charger ideal for overnight charging. Plug your car in after dinner, and by morning, it’s ready with enough range for your daily routine — whether that’s commuting, errands, or weekend drives.
However, for EVs with larger battery packs (like 80–100 kWh), a 30A charger will take longer, so those who drive long distances daily or manage multiple EVs might consider a higher-amperage charger for faster turnarounds.
To understand why the 30A charger performs the way it does, it’s important to know the difference between AC (alternating current) and DC (direct current) charging.
Your home electrical system provides AC power, but EV batteries store DC power. That means the electricity must be converted from AC to DC before the battery can be charged. In Level 1 and Level 2 chargers, this conversion happens inside the car through a component called the onboard charger.
Let’s compare the two types of charging:
The charger supplies AC electricity, which is converted to DC by the EV’s onboard charger. The charging rate depends on the onboard charger’s capacity — typically ranging from 3.3 to 11 kW in most modern EVs.
In this case, the conversion from AC to DC happens in the charging station itself, not in the vehicle. The station directly supplies DC power to the battery, bypassing the onboard charger. Because DC fast chargers use much larger and more powerful conversion electronics, they can deliver 50–350 kW of power, making them significantly faster but also more expensive and demanding on electrical infrastructure.
Therefore, while DCFC stations can recharge most EVs to 80% in 30 minutes or less, they are not suitable for typical home use due to cost, space, and power requirements. The 30A Level 2 charger remains the sweet spot for homeowners — fast, affordable, and safe for daily use.
Installing a 30A Level 2 charger is relatively straightforward but does require professional setup to ensure safety and compliance with local electrical codes. Here’s what’s typically involved:
A 30A charger must be connected to a dedicated 240V circuit breaker. Sharing the circuit with other high-power appliances is not allowed, as this could cause overloads or tripping.
A wire gauge of 10 AWG copper is generally recommended for 30A circuits, ensuring sufficient current capacity and minimal voltage drop.
Many chargers include built-in GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) protection to prevent electrical shock, especially for outdoor installations.
Most 30A chargers come with NEMA 3R or NEMA 4-rated enclosures, meaning they are resistant to rain and dust. Wall-mounted or pedestal options can fit different installation spaces.
In many regions, an electrical permit is required. It’s also advisable to have the installation inspected to ensure compliance with NEC and local building codes.
A professional electrician can typically complete installation in 2–4 hours, depending on the home’s layout and panel accessibility.
The total cost of installing a 30A charger includes both the equipment and the installation. On average:
Charger price: $400 – $800
Installation cost: $500 – $1,500 (depending on distance from panel, wiring, and permits)
Total estimated cost: $900 – $2,300
In return, users get a reliable, energy-efficient charging setup. Since most EVs are plugged in overnight, when electricity rates are lower, charging costs are minimal. For example, charging a 60 kWh battery from 20% to 100% at $0.13/kWh would cost about $6.24, giving roughly 220 miles of range.
Many chargers also feature smart charging functions, allowing users to schedule charging sessions, monitor energy usage, and adjust current levels through mobile apps. Some even integrate with home energy management systems or solar panels, optimizing electricity use and reducing costs further.
Whether a 30A charger is “enough” depends on several factors: your driving habits, vehicle type, and charging frequency.
If you drive less than 60–80 miles per day, a 30A charger is more than sufficient. Most EVs will easily regain that range in about 3–4 hours of charging, keeping your battery topped up overnight.
Smaller-battery EVs (e.g., Nissan Leaf, Chevy Bolt, Mini Cooper SE) can fully charge overnight on a 30A charger. For larger-battery models like Tesla Model S or Rivian R1T, it will take longer, but still manageable if charged regularly.
For households with multiple EVs, a single 30A charger might not be enough if both vehicles need to charge simultaneously. In that case, consider a dual charging setup or a higher-amperage charger (40A or 48A).
If you need to quickly recharge your vehicle within a few hours, perhaps for back-to-back trips or business use, a faster charger may be preferable. However, for typical overnight charging, 30A remains ideal.
In most scenarios, a 30A charger strikes the perfect balance — fast enough for everyday use without overwhelming your home’s electrical system.
Cost-Effective – Affordable to purchase and install, offering great value for homeowners.
Reliable Performance – Provides steady, efficient charging without stressing the electrical system.
Universal Compatibility – Works with nearly all EVs in North America using the J1772 connector.
Compact and Durable – Easy to install indoors or outdoors with weatherproof casings.
Smart Features – Many models support Wi-Fi/Bluetooth connectivity, load balancing, and remote control.
Energy Efficient – Uses lower power compared with high-output chargers, reducing energy costs.
Despite its advantages, a 30A EV charger isn’t perfect for everyone.
Slower for Large Batteries: Vehicles with very large batteries may take 10+ hours to fully charge.
Limited Power for Future EVs: As newer EVs with higher charging capabilities enter the market, 30A may become less future-proof.
Single-Use Limitation: Households with multiple EVs may experience scheduling conflicts unless they install multiple chargers or use load-sharing systems.
Still, for most single-EV owners today, these are minor concerns compared to the charger’s convenience and affordability.
|
Specification |
30A Level 2 |
40A Level 2 |
48A Level 2 |
|
Circuit Breaker |
40A |
50A |
60A |
|
Power Output |
~7.2 kW |
~9.6 kW |
~11.5 kW |
|
Range per Hour |
18–22 miles |
25–30 miles |
30–35 miles |
|
Ideal For |
Standard EVs, daily commutes |
Larger EVs, faster charging |
High-end EVs, fleet use |
|
Cost |
Low |
Medium |
High |
While 40A and 48A chargers offer faster speeds, they also require heavier wiring, larger breakers, and more expensive installations. For most homeowners, the added cost may not justify the modest time savings.
So, is a 30A EV charger enough? For most drivers, the answer is yes.
A 30A Level 2 charger provides a perfect middle ground between affordability, charging speed, and electrical compatibility. It offers all the power needed for daily driving needs, supports a broad range of electric vehicles, and can be conveniently installed in most homes without requiring major electrical upgrades.
As EV adoption continues to rise and home charging becomes the norm, the 30A charger will remain a dependable and practical solution for millions of drivers — combining performance, safety, and value in one efficient package.