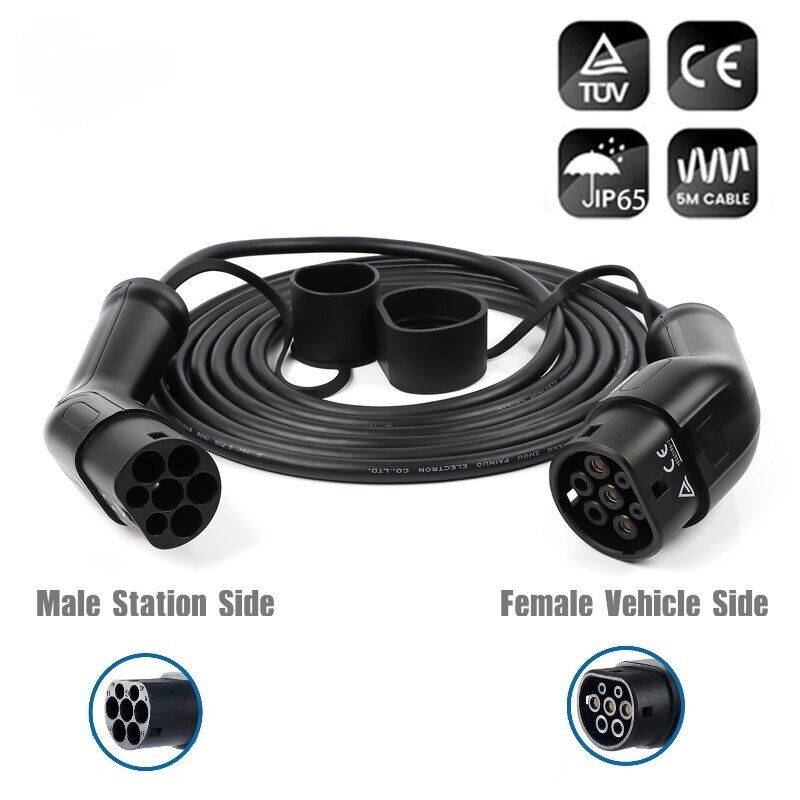
As electric vehicles (EVs) become an increasingly common sight on roads across the globe, the need for efficient, safe, and standardized charging solutions continues to grow. One of the most essential tools in any EV owner’s kit is the Mode 3 EV charging cable, often referred to as the Type 2 charging cable.
This cable has quickly become the industry standard for AC EV charging in public and residential settings. Whether you're plugging into a street-side charging station or your wall-mounted home charger, the Mode 3 cable plays a central role in delivering power to your vehicle in a safe and controlled manner.
With the rise of electrified transportation and increased demand for reliable charging infrastructure, understanding the function, compatibility, and benefits of Mode 3 cables is crucial for both current and prospective EV owners.
The Mode 3 charging cable is designed specifically for alternating current (AC) charging and is widely used across Europe and other parts of the world. Unlike DC fast charging—which delivers power directly to the battery—Mode 3 relies on the vehicle’s onboard charger to convert AC to DC.
Mode 3 cables are typically used in conjunction with dedicated EV charging stations, either at home or in public spaces. These charging setups are ideal for everyday use, such as overnight home charging or mid-day top-ups at office parking lots.

AC Charging Only: Designed exclusively for AC charging.
Smart Communication: Incorporates control and protection protocols for safe charging.
Removable Cable: Unlike tethered charging stations, Mode 3 cables are often separate and portable.
One of the first things to understand about Mode 3 cables is the connector type, which depends largely on your vehicle's region of origin.
Primarily found in North American and Asian markets.
Supports single-phase charging only.
Typically includes a latch to prevent accidental disconnection.
Standard in Europe and compatible with both single-phase and three-phase systems.
Features seven pins to support higher power levels and data communication.
Type 2 is the connector of choice for most European automakers and public charging stations.
Because of its flexibility and broader compatibility, the Type 2 connector has become the go-to solution for manufacturers and charging station providers across the EU.
Another major consideration is the length of the charging cable, which affects where your vehicle must be positioned in relation to the charging port.
Most Mode 3 cables range from 5 to 10 meters, offering enough length to accommodate a variety of parking arrangements—whether you’re pulling into a garage, reversing into a driveway, or using a public curbside charger.
Longer cables provide added convenience, especially in urban environments or shared parking areas, where charging stations may not always be adjacent to your vehicle.
Mode 3 cables are available in various power ratings, typically between 3.6 kW and 22 kW, depending on the electrical system and whether it's single-phase or three-phase.
Common for home charging setups.
Suitable for overnight charging, with a full charge taking between 6 to 8 hours, depending on your EV’s battery size.
Ideal for regular daily use, allowing you to charge your vehicle while you sleep.
Found at public charging stations and in some advanced home systems.
Can reduce charging time dramatically—often fully charging an EV in 2 to 3 hours.
Supports larger vehicles or those with higher onboard charging capacities.
Keep in mind that actual charging time is influenced by several factors, including:
The EV’s onboard charger rating
The output capacity of the charging station
The battery’s current state of charge
Ambient temperature conditions
Many first-time EV owners may wonder how Mode 3 charging compares to the more basic Mode 2 solution.
Often come as standard accessories with EVs.
Feature a domestic plug (e.g., Schuko) on one end and a Type 1 or Type 2 plug on the other.
Plug directly into standard household sockets.
Offer slow charging speeds, often taking 10 to 14 hours for a full charge.
Usually have built-in safety features, such as current sensors and temperature monitors.
While Mode 2 charging is convenient in a pinch, it's generally not ideal for long-term use due to lower efficiency and longer charging times.
Require a dedicated EV charging station, either wall-mounted or free-standing.
Feature built-in communication systems that exchange data with the EV to ensure safe charging.
Offer faster and safer charging with higher power ratings and better current regulation.
Are commonly used at both public and private charging locations.
In summary, while Mode 2 chargers are good for occasional use or emergencies, Mode 3 chargers are far better suited for regular, reliable, and efficient EV charging.
Over the past few years, Mode 3 has become the de facto standard for EV charging in Europe and many other markets due to its safety, speed, and smart communication features.
Safe and Smart: Communicates with the vehicle to manage power flow and protect against overcurrent or overheating.
Flexible Power Range: Works across different charging speeds and electrical systems.
Future-Proof: Supports newer EVs and higher capacities as battery technology improves.
Compatibility: Widely compatible with home chargers, workplace stations, and public charging networks.
Additionally, with the global push toward greener mobility and smarter infrastructure, Mode 3 cables are often integrated with smart home energy systems, allowing for features like scheduled charging, off-peak power use, and load balancing.
One of the defining features of Mode 3 charging is its focus on user and equipment safety. The system is designed to minimize the risks associated with electrical charging, such as:
Overheating
Short circuits
Power surges
Incorrect connections
Mode 3 chargers come equipped with built-in protections, including:
Residual current devices (RCDs)
Circuit breakers
Communication protocols to ensure that charging only begins once a secure connection is confirmed
These features help safeguard not only the EV but also the electrical grid and the user.
As EV adoption continues to rise, governments and private sectors are investing heavily in charging infrastructure, with Mode 3 chargers leading the way.
Across Europe, new building regulations increasingly require residential and commercial properties to be EV-ready, meaning they must support Mode 3 installations. Similarly, automakers are standardizing on Type 2 connectors for their European models, further driving Mode 3 dominance.
Some key market trends include:
Growth in private charging stations: More homeowners are installing Mode 3 wall boxes to support daily charging routines.
Expansion of public networks: Urban centers and highway corridors are being equipped with more Mode 3-compatible AC chargers.
Integration with renewable energy: Mode 3 systems are increasingly linked to solar panels and battery storage for sustainable charging.
The Mode 3 EV charging cable is far more than just a wire—it’s the link between your vehicle and the future of sustainable transport. Offering speed, safety, and smart connectivity, Mode 3 has earned its place as the preferred solution for AC charging at homes, offices, and public spaces.
Whether you're a new EV owner or an experienced driver looking to upgrade your charging setup, investing in a high-quality Mode 3 cable is essential. With growing infrastructure, expanding public networks, and increasing vehicle compatibility, the Mode 3 charging standard is here to stay—and it’s driving us toward a cleaner, more efficient future.