As electric vehicles (EVs) continue to grow in popularity, understanding the technology behind EV charging is becoming increasingly important for both consumers and businesses. Two primary types of EV chargers dominate the market: single-phase and three-phase chargers. Each type comes with distinct advantages, limitations, and applications. Let’s delve into the differences, suitability, and considerations surrounding single-phase and three-phase EV chargers.
A single-phase EV charger operates on a single alternating current (AC) waveform. This type of charger is the standard for most residential electrical systems and is commonly installed in homes.
Single-phase chargers typically provide power outputs ranging from 3.7 kW to 7.4 kW. This translates to adding 3.7 to 7.4 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of energy to an EV battery for each hour of charging. Depending on the charger’s capacity and the vehicle’s compatibility, charging an EV with a single-phase charger is slower compared to its three-phase counterpart. For instance, it may take several hours to fully charge a medium-sized EV battery using a single-phase charger.
These chargers require only one “hot wire” for operation. They are simple to install and suitable for homes with standard electrical service, making them a popular choice for residential EV owners.
A three-phase EV charger, on the other hand, utilizes three alternating current waveforms. This configuration is common in commercial and industrial settings and can also be found in some residential properties with advanced electrical systems.
Three-phase chargers deliver significantly higher power, ranging from 11 kW to 22 kW, and can go even higher in specific setups. This means they can add 11 to 22 kWh of energy to an EV battery in just one hour, drastically reducing charging times. For example, a battery that might take 8 to 10 hours to charge using a single-phase charger could be charged in as little as 2 to 3 hours with a three-phase charger.
Three-phase chargers require three “hot wires” to operate. They demand a balanced load from the power grid, evenly distributing the electrical current across all three phases. This balanced distribution enhances efficiency and reduces strain on the electrical system.
The most notable difference between single-phase and three-phase EV chargers is charging speed. Single-phase chargers are ideal for overnight charging at home, where time is not a critical factor. In contrast, three-phase chargers are designed for rapid charging, making them more suitable for commercial use or scenarios where quick turnarounds are needed.
Single-Phase Chargers: Best suited for residential settings with standard electrical systems. They are sufficient for daily commuting needs and are compatible with most home electrical setups.
Three-Phase Chargers: Ideal for commercial properties, EV fleets, and homes with advanced electrical systems. They are also more suited for high-capacity EVs that require faster charging times.
The cost of installation and operation varies between the two types. Single-phase chargers are generally more affordable and easier to install. Three-phase chargers, while offering superior performance, often come with higher installation and operational costs due to their complexity and the need for a more robust electrical system.
Three-phase chargers are more efficient in delivering power due to their balanced load distribution across three wires. This efficiency results in less energy loss and lower operational costs in the long run, particularly for heavy-duty charging applications.
Interestingly, three-phase EV cables can be used for single-phase charging, but the reverse is not possible. If you primarily intend to use the cable at home, it’s essential to consider the kW capacity of your home’s charging post to ensure compatibility. Choosing a three-phase cable provides more flexibility for future use, especially if you plan to upgrade your charging system or use public charging stations.
Type 1 charging cables are designed exclusively for single-phase charging. They are becoming increasingly rare, as most modern EVs and charging systems use Type 2 connectors. However, certain models, such as the Kia Soul EV, Citroen C-Zero, and Peugeot iOn, still feature Type 1 ports. The maximum power output for Type 1 cables is 7.4 kW.
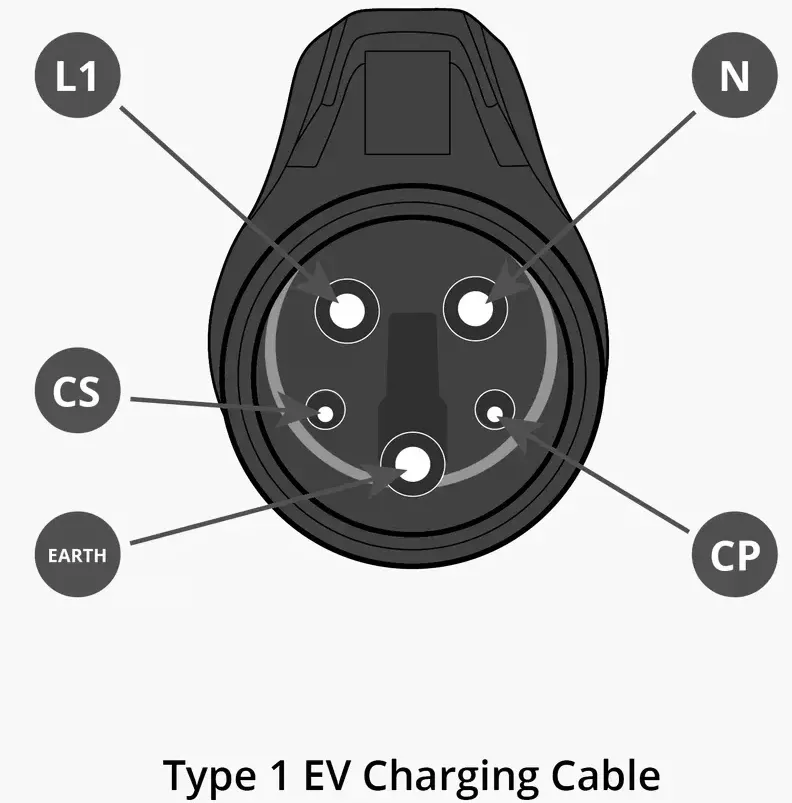
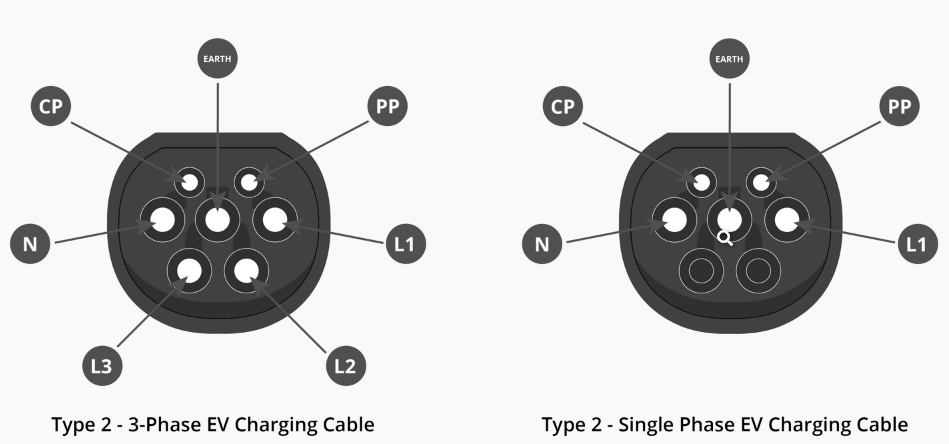
Type 2 charging cables are versatile and widely used in both single-phase and three-phase charging systems. These cables come in two variants:
Single-Phase Type 2 Cables: Designed for single-phase charging only.
Three-Phase Type 2 Cables: Support both single-phase and three-phase charging, offering greater flexibility.
To select the right cable, ensure it matches the number of phases supported by your vehicle and charging system. For instance, if you have access to three-phase charging, opting for a three-phase cable is recommended to maximize efficiency and future-proof your setup.
When selecting an EV charger, consider the following factors:
Ensure your home’s electrical system can support the charger’s power requirements.
Verify the maximum charging capacity of your EV and select a charger that matches or complements it.
Determine how often and how quickly you need to charge your vehicle. Single-phase chargers are ideal for regular overnight charging, while three-phase chargers are better for frequent or rapid charging.
Future Considerations: If you plan to upgrade your EV or install a more advanced charging system, investing in a three-phase charger and compatible cable might be a smart move.
Understanding the differences between single-phase and three-phase EV chargers is essential for making an informed decision about your EV charging setup. Single-phase chargers offer a cost-effective and straightforward solution for residential use, while three-phase chargers provide faster and more efficient charging for high-demand scenarios. Additionally, choosing the right type of charging cable and ensuring compatibility with your vehicle and charging station can further enhance your EV ownership experience.
As the adoption of electric vehicles continues to rise, advancements in charging technology will likely offer even more options and features, ensuring that there’s a suitable solution for every driver’s needs.