As the world shifts towards sustainable energy solutions, electric vehicles (EVs) have emerged as a cornerstone of the green revolution. Central to the functionality of EVs is the charging infrastructure, with EV plugs playing a pivotal role. But what exactly are EV plugs, and how do they differ across regions and vehicle brands? This article delves into the intricacies of EV charging plugs, exploring their types, functionalities, and the standards that govern them.
An EV charging plug is the interface that connects an electric vehicle to a charging station, facilitating the transfer of electricity to the vehicle's battery. Much like the plugs used for household appliances, EV plugs are designed to deliver power efficiently and safely. However, unlike standard household plugs, EV plugs are tailored to meet the specific requirements of electric vehicles, which vary based on the vehicle's make, model, and the charging level.
EV charging plugs are not one-size-fits-all; they differ significantly depending on the region, the type of charging (Level 1, Level 2, or Level 3), and the vehicle manufacturer. This diversity in plug types can be attributed to the varying electrical standards and infrastructure across different parts of the world. In the following sections, we will explore the different types of EV plugs, their unique features, and the regions where they are predominantly used.
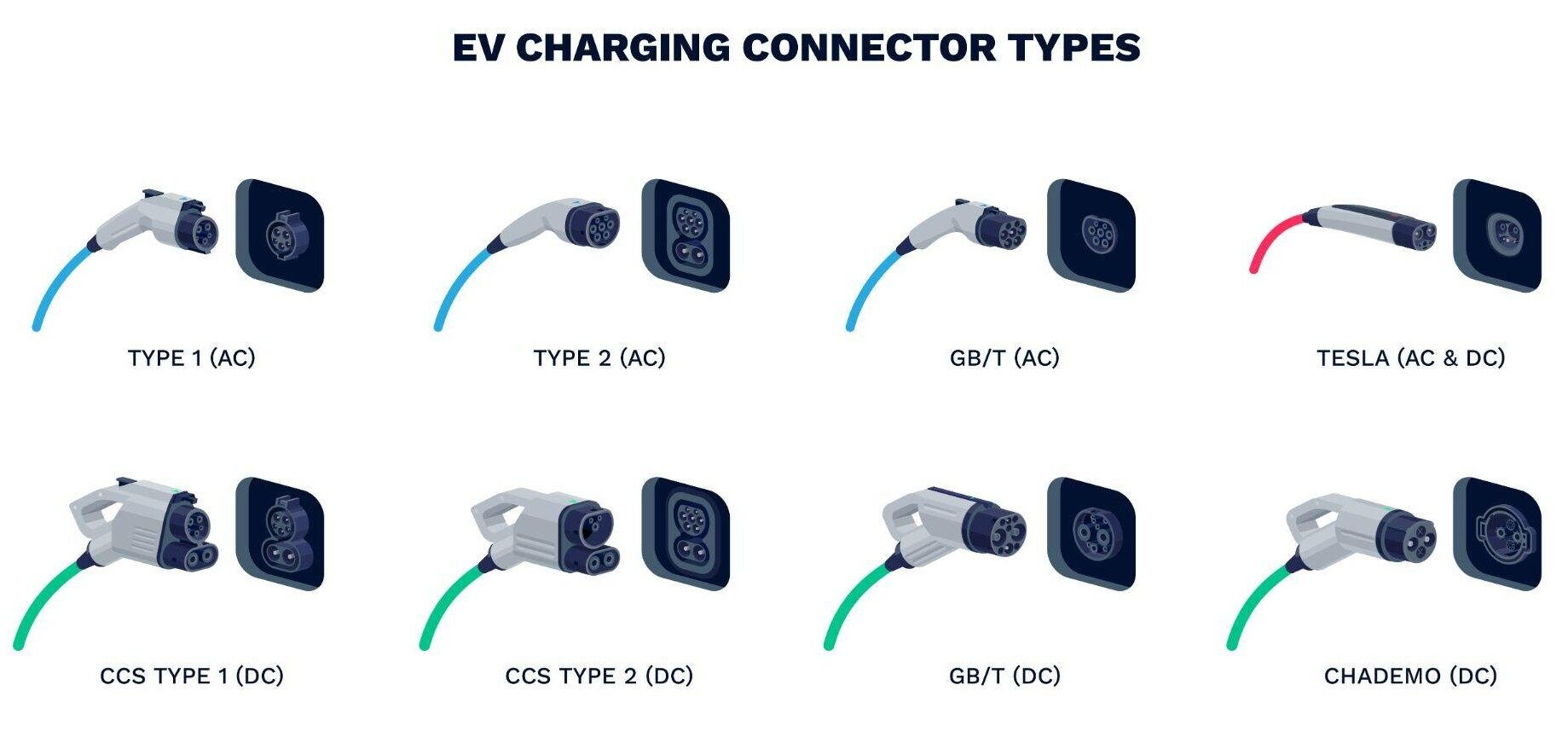
Level 1 and Level 2 charging are the most common forms of EV charging, typically used for home charging and public charging stations. These levels of charging utilize alternating current (AC) and are characterized by their relatively slower charging speeds compared to Level 3 or DC fast charging. The two primary types of AC charging plugs are Type 1 (SAE J1772) and Type 2 (Mennekes).
The Type 1 plug, also known as the SAE J1772, is the standard for Level 1 and Level 2 charging in North America and parts of Asia. This plug is designed for single-phase AC power, which is the standard in these regions. The Type 1 plug features a 5-pin configuration and can deliver power up to 19.2 kW, making it suitable for most residential and public charging needs.
In practical terms, if you own an electric vehicle in the United States, chances are you will use a Type 1 plug to connect your car to a home charging station or a public charging point. The widespread adoption of the Type 1 plug in North America has made it a reliable and convenient option for EV owners in the region.
In contrast to the Type 1 plug, the Type 2 plug, commonly referred to as the Mennekes plug, is the standard for Level 1 and Level 2 charging in Europe. The Type 2 plug is designed for three-phase AC power, which is the default power source in Europe. This 7-pin plug can deliver power up to 43 kW, significantly higher than the Type 1 plug.
One of the standout features of the Type 2 plug is its automatic locking mechanism, which prevents accidental disconnection during charging. This feature enhances the safety and reliability of the charging process, making the Type 2 plug a preferred choice in Europe. Additionally, the Type 2 plug's compatibility with three-phase power allows for faster charging times, which is particularly beneficial for EV owners who require quicker charging solutions.
While Level 1 and Level 2 charging are sufficient for most daily charging needs, Level 3 or DC fast charging is essential for long-distance travel and quick top-ups. DC fast charging plugs are designed to deliver direct current (DC) power directly to the vehicle's battery, bypassing the onboard charger and significantly reducing charging times. The most common types of DC fast charging plugs are CCS (Combined Charging System), CHAdeMO, GB/T, and Tesla Supercharger.
The Combined Charging System (CCS) is a fast-charging standard that has gained widespread adoption, particularly in North America and Europe. The CCS plug is unique in that it combines the Type 1 or Type 2 AC charging plug with additional pins for DC fast charging. This combination allows for a single plug to handle both AC and DC charging, simplifying the charging process for EV owners.
CCS1 is the variant of the Combined Charging System used in North America. It integrates the Type 1 (SAE J1772) plug with two additional DC pins, enabling fast charging capabilities. CCS1 is compatible with most electric vehicles in North America and is commonly found at public fast-charging stations.
In Europe, the CCS2 plug is the standard for fast charging. Similar to CCS1, CCS2 combines the Type 2 (Mennekes) plug with two additional DC pins. This configuration allows for high-speed charging and is compatible with a wide range of electric vehicles in Europe. The CCS2 plug's ability to deliver power up to 350 kW makes it one of the fastest charging options available.
CHAdeMO is another fast-charging standard, primarily used by Japanese automakers such as Nissan and Mitsubishi. The CHAdeMO plug is distinct from the CCS plug and is characterized by its unique design and high-power delivery capabilities. While CHAdeMO was one of the first fast-charging standards, its adoption has been somewhat limited outside of Japan. However, it remains a reliable option for EV owners with compatible vehicles.
The GB/T standard is the predominant fast-charging standard in China. Developed by the Chinese government, the GB/T plug is designed to meet the specific needs of the Chinese market. It supports both AC and DC charging and is compatible with a wide range of electric vehicles in China. The GB/T standard has played a crucial role in the rapid expansion of China's EV infrastructure, making it one of the largest markets for electric vehicles in the world.
Tesla, a pioneer in the electric vehicle industry, has developed its proprietary charging standard known as the Tesla Supercharger. The Tesla Supercharger plug is unique in that it accommodates Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3 charging, supporting both AC and DC power. In North America, Tesla vehicles use the NACS (North American Charging Standard) plug, which is compatible with the Type 1 (SAE J1772) plug via an adapter. In Europe, Tesla has transitioned to using the CCS2 plug for its vehicles, aligning with the regional standard.
The Tesla Supercharger network is renowned for its high-speed charging capabilities, with some stations delivering power up to 250 kW. This allows Tesla vehicles to achieve significant range in a short amount of time, making long-distance travel more convenient for Tesla owners.

The world of EV plugs is diverse and complex, reflecting the varying electrical standards and infrastructure across different regions. From the Type 1 and Type 2 plugs used for AC charging to the CCS, CHAdeMO, GB/T, and Tesla Supercharger plugs designed for fast charging, each type of plug has its unique features and applications.
As the adoption of electric vehicles continues to grow, the development of standardized and interoperable charging solutions will be crucial. The evolution of EV plugs and charging infrastructure will play a significant role in shaping the future of transportation, making it more sustainable and accessible for all.
In conclusion, understanding the different types of EV plugs and their functionalities is essential for EV owners and enthusiasts alike. Whether you're charging at home, at a public station, or on a long road trip, knowing which plug to use and how it works can enhance your EV experience and contribute to the broader transition towards a greener future.