As electric vehicles (EVs) become a permanent feature of global transportation, charging infrastructure is evolving just as rapidly. While much attention has been given to home garages and private charging solutions, a major shift is taking place outside buildings, parking structures, and commercial spaces. Outdoor electric car chargers are emerging as a critical pillar of the EV ecosystem, providing reliable, accessible, and scalable charging where people live, work, shop, and travel.
From apartment complexes and office parks to retail centers, hotels, and municipal parking lots, outdoor charging stations are redefining how drivers interact with electric mobility. They are not simply an alternative to indoor chargers—they represent a strategic solution for urban planning, business growth, and sustainable development.
This article explores what outdoor electric car chargers are, why they matter, their key benefits, technical considerations, ideal applications, and how they support the transition to a low-carbon transportation future.
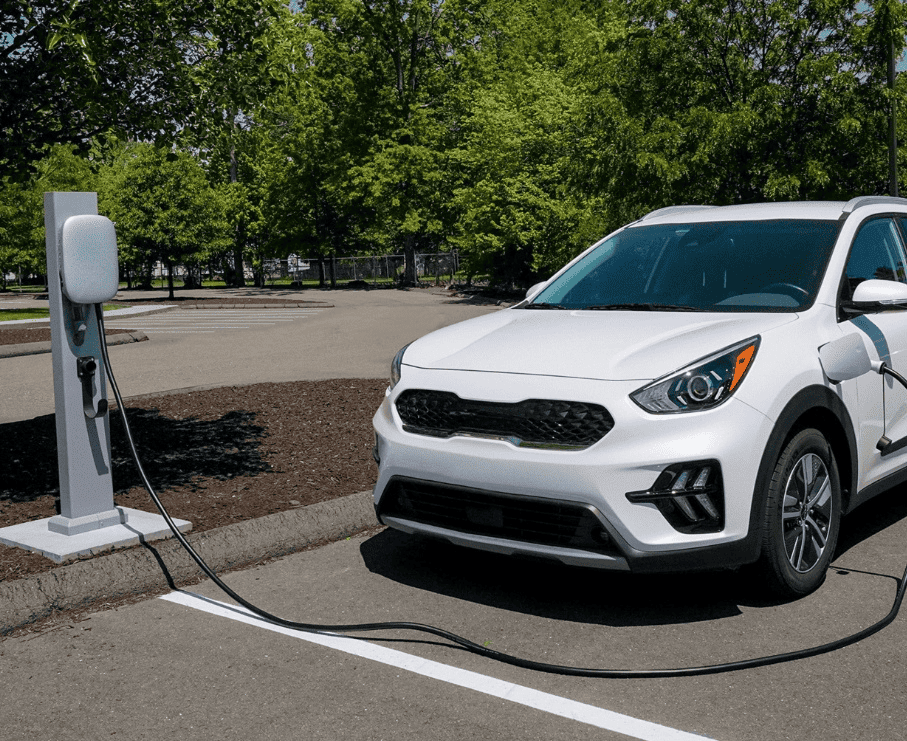
An outdoor electric car charger is a charging unit designed specifically to operate in open-air environments. Unlike indoor chargers, which are installed inside garages or enclosed parking structures, outdoor chargers are built to withstand weather conditions such as rain, heat, cold, dust, and humidity. They feature durable housings, sealed components, and certified protection ratings to ensure safety and performance over long service lifespans.
Outdoor chargers are available in multiple configurations, including:
- AC Level 2 chargers (typically 7 kW–22 kW), suitable for workplaces, residential complexes, and long-stay parking
- DC fast chargers (30 kW–350 kW), ideal for commercial locations, highways, fleet depots, and rapid-turnover environments
- Wall-mounted units, pedestal-mounted chargers, and integrated charging stations with screens and payment systems
They support common charging standards such as Type 1, Type 2, CCS, CHAdeMO, and GB/T, making them compatible with a wide range of EV models across different markets.
The rapid adoption of electric vehicles has outpaced the growth of traditional home charging. In many urban environments, especially high-density cities, a significant percentage of residents do not have access to private garages or dedicated parking spaces. This creates a charging gap that cannot be solved by indoor installations alone.
Outdoor charging infrastructure addresses this challenge by placing chargers directly where vehicles are already parked: in shared parking lots, curbside spaces, commercial properties, and public facilities. As governments introduce stricter emissions regulations and businesses pursue carbon-reduction strategies, outdoor chargers are becoming a fundamental component of modern infrastructure planning.
While indoor chargers offer protection and convenience, outdoor electric car chargers in multi-residential and commercial spaces provide a unique set of advantages that directly support accessibility, scalability, and sustainability.
One of the most important benefits of outdoor EV chargers is greater accessibility. Not all drivers have access to private garages or indoor parking facilities. In apartment complexes, condominiums, and shared residential developments, parking may be limited or located in open lots rather than enclosed structures.
Outdoor chargers allow property owners, building managers, and municipalities to make EV charging available to:
- Residents without assigned indoor parking
- Tenants in multi-family housing
- Employees in office complexes
- Visitors to shopping centers, hotels, and public facilities
By installing chargers in visible, open areas, property operators remove barriers to EV adoption and ensure that more people can participate in electric mobility.
In many urban and high-density environments, space is a premium resource. Parking garages are often overcrowded, and indoor areas are needed for storage, mechanical systems, or building services. Installing chargers indoors can require significant renovation, structural adjustments, and electrical upgrades.
Outdoor chargers offer a space-efficient alternative. They can be installed:
- Along perimeter parking areas
- In surface parking lots
- Near building entrances
- At curbside locations
This allows property owners to free up valuable indoor space for other uses while still providing robust charging capacity. In commercial settings, it also helps optimize traffic flow by distributing chargers throughout large parking areas rather than concentrating them in one location.
Outdoor charging solutions provide exceptional flexibility in placement. Unlike indoor installations, which are constrained by building layouts, ceiling heights, and internal wiring routes, outdoor chargers can be positioned wherever electrical access and parking availability allow.
This flexibility enables:
- Installation of a higher number of charging points across large properties
- Strategic placement near high-traffic zones for maximum visibility and usage
- Phased deployment, where additional chargers can be added as EV adoption grows
For property developers and commercial operators, this scalability is essential. Outdoor chargers can be installed as part of new construction projects or retrofitted into existing properties with minimal disruption.
Sustainability is no longer a niche concern—it is a central factor in consumer and tenant decision-making. Providing EV charging options enhances the environmental profile of a property or business, making it more attractive to eco-conscious residents, employees, and customers.
For residential developments, outdoor chargers can:
- Increase property value
- Improve tenant retention
- Differentiate the building in competitive housing markets
For commercial properties, they offer:
- Increased foot traffic from EV drivers
- Longer customer dwell times while vehicles charge
- A visible commitment to environmental responsibility
In corporate settings, outdoor EV charging supports sustainability goals, ESG reporting, and employer branding, reinforcing the organization’s commitment to reducing carbon emissions.
Beyond the core benefits, outdoor electric car chargers offer several additional advantages that make them especially attractive for public and semi-public environments.
Compared to indoor installations, outdoor chargers often involve lower installation costs. They typically require:
- Less structural modification
- Simplified cabling routes
- Reduced ventilation and fire-safety requirements
For many projects, especially retrofits, outdoor deployment can be completed faster and at a lower total cost, enabling quicker return on investment.
Outdoor chargers are highly visible, serving as a physical symbol of a property’s or business’s commitment to sustainability and innovation. Many modern chargers feature:
- Branded housings
- Digital screens for information or advertising
- LED lighting for nighttime visibility
This visibility not only promotes EV usage but also enhances brand image, particularly for retail centers, hotels, and corporate campuses.
Outdoor chargers can be easily integrated into public or semi-public charging networks, enabling:
- Mobile app-based access
- Contactless payment systems
- Usage tracking and remote management
This makes them ideal for municipalities, parking operators, and fleet managers who need centralized control, data analytics, and revenue generation.
To ensure safe and reliable operation, outdoor electric car chargers must meet strict technical requirements. When selecting and deploying outdoor charging infrastructure, several key factors should be considered.
Outdoor chargers are exposed to rain, snow, dust, heat, and temperature fluctuations. High-quality units typically carry IP54, IP65, or higher protection ratings, ensuring resistance to water ingress and solid particles.
Durable materials such as corrosion-resistant steel, aluminum, and UV-stabilized plastics are commonly used to extend service life in harsh environments.
Outdoor installations must comply with national and international electrical safety standards. Features typically include:
- Residual current devices (RCDs)
- Ground-fault protection
- Overvoltage and surge protection
- Emergency stop functions
Compliance with standards such as IEC 61851, IEC 62196, UL certifications, and regional electrical codes is essential to ensure safe operation.
Modern outdoor chargers are often “smart chargers” equipped with:
- Ethernet, Wi-Fi, or 4G/5G connectivity
- Remote monitoring and diagnostics
- Load management and power sharing
- User authentication and billing systems
These features allow operators to optimize energy use, prevent grid overload, and manage large networks efficiently.
Outdoor chargers are highly versatile and can be deployed across a wide range of environments.
Apartment complexes, condominiums, and housing developments benefit from outdoor chargers by offering residents shared access to charging without requiring individual garage installations.
Shopping malls, supermarkets, restaurants, and entertainment venues can use outdoor chargers to attract EV-driving customers and increase visit duration.
Workplace charging supports employee satisfaction, encourages sustainable commuting, and helps companies meet environmental goals.
Hotels, resorts, and tourist attractions can differentiate their services by offering convenient outdoor charging for guests traveling in electric vehicles.
Municipal parking lots, street-side parking, transit hubs, and community centers are ideal locations for outdoor charging, supporting citywide EV adoption.
Outdoor electric car chargers play a direct role in reducing transportation-related emissions. By expanding access to charging in shared and public spaces, they help accelerate the shift away from internal combustion engines.
Additionally, many outdoor charging systems can be integrated with:
- Renewable energy sources, such as solar canopies over parking lots
- Energy storage systems for peak-load management
- Smart grids that balance demand and supply
This integration further enhances their contribution to a cleaner, more resilient energy infrastructure.
Despite their advantages, outdoor EV chargers also present challenges that must be carefully managed.
Publicly accessible equipment can be vulnerable to damage or misuse. To address this, manufacturers and operators use:
- Lockable enclosures
- Tamper-resistant hardware
- Surveillance and lighting
- Remote monitoring alerts
Large numbers of chargers can strain local electrical infrastructure. Smart load management, power sharing, and energy storage solutions are increasingly used to balance demand and avoid costly grid upgrades.
Outdoor installations often require permits, zoning approvals, and coordination with utilities. Streamlined regulations and standardized designs are helping reduce deployment timelines.
As EV adoption continues to rise, outdoor charging infrastructure will become even more critical. Future developments are expected to include:
- Ultra-fast DC chargers capable of delivering hundreds of kilometers of range in minutes
- Solar-integrated charging stations for energy self-sufficiency
- Vehicle-to-grid (V2G) functionality, allowing EVs to support grid stability
- AI-driven energy management for predictive maintenance and optimal power distribution
Governments, developers, and businesses are increasingly recognizing that outdoor chargers are not merely accessories but foundational components of modern transportation networks.
Outdoor electric car chargers are transforming how and where electric vehicles are powered. By increasing accessibility, maximizing space utilization, offering flexible installation, and appealing to eco-conscious users, they provide a practical and scalable solution for the growing EV market.
From residential complexes and commercial centers to public infrastructure and corporate campuses, outdoor chargers enable widespread charging access while supporting sustainability goals and long-term urban development. As technology advances and demand continues to grow, these open-air charging solutions will play a central role in shaping the future of electric mobility.
In the transition to cleaner transportation, outdoor electric car chargers are not just infrastructure—they are enablers of a more accessible, efficient, and sustainable mobility ecosystem.