Electric vehicles (EVs) are rapidly becoming a mainstream mode of transportation, and with this shift comes the need to understand the technology that powers them. One of the most critical components of EV infrastructure is the charging plug. Much like the plugs used for household appliances, EV charging plugs connect to the vehicle’s socket to deliver power to the battery. However, unlike standard household plugs, EV charging plugs vary significantly depending on the vehicle brand, charging level, and regional standards. This article delves into the different types of EV charging plugs, their functionalities, and their compatibility across various vehicles and charging networks.

An EV charging plug is the interface between the charging station and the electric vehicle. It serves as the conduit through which electricity flows to recharge the vehicle’s battery. While the concept is similar to plugging in a household appliance, EV charging plugs are designed to handle higher power levels and are tailored to specific charging standards. These plugs differ based on the type of current they deliver (alternating current or direct current), the charging speed, and the vehicle manufacturer’s specifications.
The diversity in EV charging plugs can be attributed to the varying needs of different vehicles and the evolving technology in the EV industry. Understanding these differences is crucial for EV owners to ensure compatibility and optimize charging efficiency.
EV charging is broadly categorized into two types: alternating current (AC) charging and direct current (DC) charging. Each type serves different purposes and is suited for specific scenarios.
AC charging is the most common form of EV charging and is typically used for daily charging needs. It is divided into two levels: Level 1 and Level 2.
Level 1 charging is the simplest and slowest form of AC charging. It involves plugging the EV into a standard 120-volt household outlet using the cable provided with the vehicle. While convenient, Level 1 charging adds only about 3 to 5 miles of range per hour, making it ideal for overnight charging or for drivers with minimal daily mileage.
Level 2 charging is significantly faster and requires a dedicated charging station, such as the ChargePoint Home Flex. These stations use a 240-volt power source and can deliver up to 40 miles of range per hour. Level 2 chargers are commonly found at homes, workplaces, and public charging stations, making them a practical choice for most EV owners.
In North America, two connector standards are used for AC charging:
SAE J1772: This is the standard connector for most non-Tesla EVs in North America.
North American Charging Standard (NACS): Developed by Tesla, this connector is primarily used for Tesla vehicles but is gaining broader acceptance.
DC fast charging is the quickest way to recharge an EV, making it ideal for long-distance travel or when time is of the essence. Unlike AC charging, which relies on the vehicle’s onboard charger to convert AC power to DC, DC fast charging delivers direct current straight to the battery, significantly reducing charging times.
In North America, there are three primary types of DC fast charging plugs:
SAE Combo (CCS1): The Combined Charging System (CCS) combines the J1772 connector with two additional DC pins, allowing for both AC and DC charging through a single port.
CHAdeMO: Developed in Japan, this connector is commonly used by Nissan and Mitsubishi EVs.
NACS: Tesla’s proprietary connector supports both AC and DC fast charging, making it a versatile option for Tesla vehicles.
It’s important to note that not all EVs are compatible with DC fast charging, and compatibility depends on the vehicle’s design and the charging network.
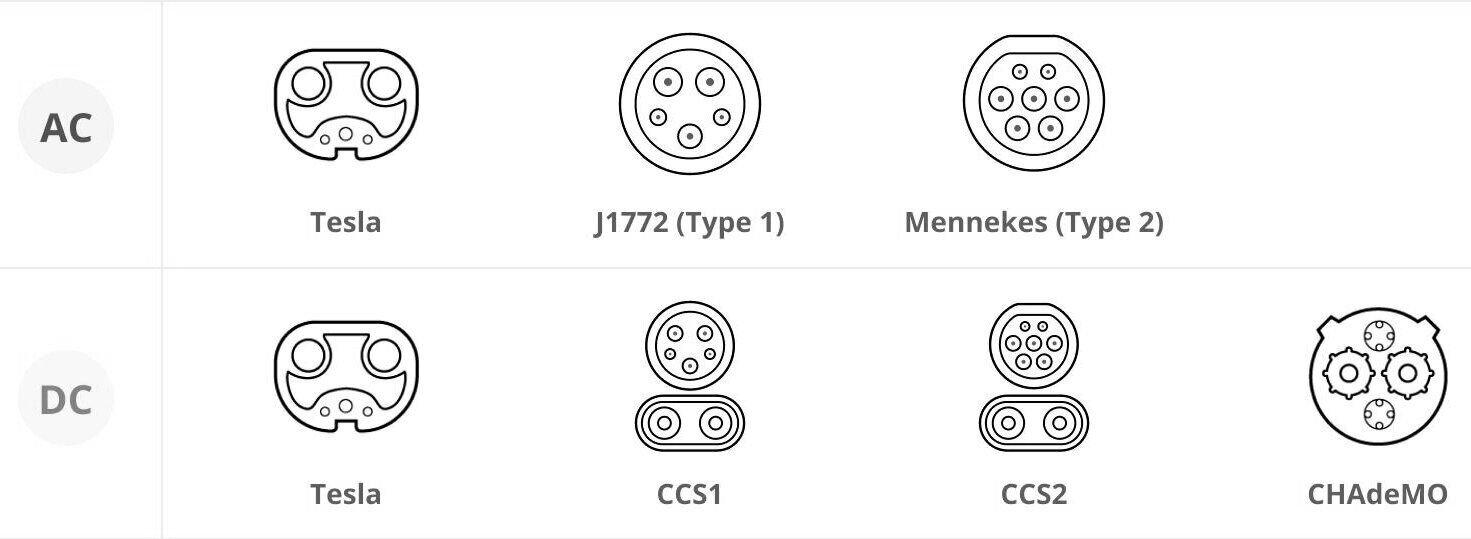
Tesla has established itself as a leader in the EV industry, and its charging infrastructure is a key part of its success. Tesla vehicles use a proprietary charging plug that is compatible with all levels of charging—Level 1, Level 2, and DC fast charging. This universal compatibility simplifies the charging process for Tesla owners, as they do not need separate connectors for different charging levels.
However, Tesla’s charging plug is not compatible with non-Tesla EVs, and vice versa. To address this, Tesla provides adapters that allow Tesla vehicles to charge at non-Tesla stations and, more recently, has opened its Supercharger network to non-Tesla EVs with the use of adapters. This move is part of Tesla’s broader strategy to promote EV adoption and expand its charging infrastructure.
The types of EV charging plugs available can vary significantly depending on the region. For example:
North America: The SAE J1772 and NACS connectors dominate the AC charging landscape, while CCS1, CHAdeMO, and NACS are used for DC fast charging.
Europe: The Type 2 connector (Mennekes) is the standard for AC charging, and CCS2 is widely used for DC fast charging.
Asia: CHAdeMO is prevalent in Japan, while China has developed its own GB/T standard for both AC and DC charging.
These regional differences highlight the need for standardization in the EV industry to ensure seamless charging experiences for drivers worldwide.
As the EV market continues to grow, the industry is moving toward greater standardization and interoperability. Tesla’s decision to open its Supercharger network to non-Tesla vehicles is a significant step in this direction. Additionally, efforts are underway to develop universal charging standards that can accommodate all types of EVs, regardless of the manufacturer.
Wireless charging technology is also emerging as a potential game-changer, eliminating the need for physical plugs altogether. While still in its early stages, wireless charging could revolutionize the way EVs are powered, offering a more convenient and user-friendly experience.
EV charging plugs are a vital component of the electric vehicle ecosystem, enabling drivers to recharge their vehicles efficiently and conveniently. From AC charging for daily use to DC fast charging for long-distance travel, the variety of plugs and connectors reflects the diverse needs of EV owners. As the industry evolves, greater standardization and innovation in charging technology will play a crucial role in accelerating the adoption of electric vehicles worldwide.
Understanding the different types of EV charging plugs and their compatibility is essential for both current and prospective EV owners. By staying informed about the latest developments in charging infrastructure, drivers can make the most of their electric vehicles and contribute to a sustainable future.